
How Does an Electric Car Work?
Find Out How an Electric Car Engine Works
An electric car takes electricity from the national grid and stores it in rechargeable batteries. These power an electric motor which, in turn, drives the wheels.
Most electric cars are fully automatic and use a single-speed transmission. An electric motor provides more torque than an internal combustion engine (ICE) which eliminates the need for a clutch and standard transmission.
An electric motor also allows power from the engine to go directly to the wheels. This is why electric cars accelerate faster than cars with an ICE.
Find out how an electric motor works and how electric cars utilise 'regenerative braking' below.
What Are The Different Types Of Electric Cars?
There are a few different types of electric cars.
-
Plug-in Electric. This type of car works purely on electricity and doesn't use any kind of fuel. It is powered solely by a battery and doesn't use any kind of internal combustion engine.
-
Plug-in Hybrid. These kinds of vehicles run on electricity, but have a traditional fuel engine so you can still use the car once it has run out of charge. They are charged in the same way plug-in electric cars are and are a good stopgap for switching from an ICE vehicle to a fully electric one.
-
Hybrid-Electric. These cars mainly run on fuel, but also have an electric battery which is charged through regenerative braking. You can switch between the two power sources with the click of a button. They cannot be plugged in at a power source to charge.
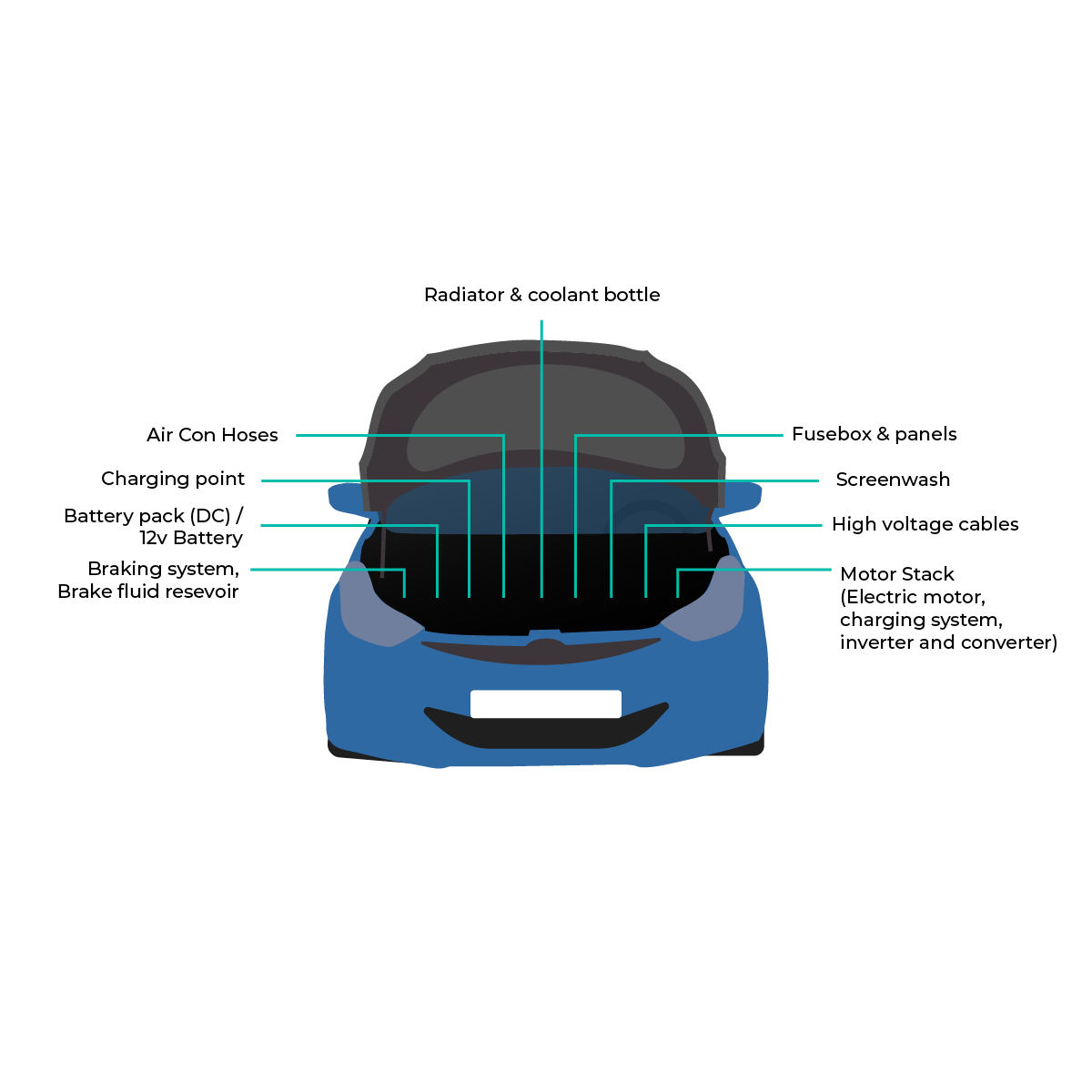
What Are The Inner Parts of an EV?
EVs have 90% fewer moving parts in comparison with an ICE vehicle. Here are the key components:
-
Electric Engine/Motor - Provides power to turn the wheels. It can be a DC/AC type, but AC motors are more common.
-
Inverter - Converts the electric current in the form of Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC)
-
Drivetrain - Most EVs have a one-speed transmission, which sends power from the motor to the wheels.
-
Batteries - Store the electricity required to run an EV. The higher the kW of the battery, the higher the range.
-
Charging - Plugs into an EV charging point to charge the battery.
How Does an Electric ‘Engine’ Work?
Electric car batteries store chemical energy and convert it to electrical energy through the flow of electrons from one material to another. However, this energy can't power an electric car.
The electric motor converts this electrical energy into mechanical energy, providing the power to drive an electric car.
They also generate torque thanks to the interaction between a magnetic field and electric current within an electromagnetic coil.
An electric motor is made up of five parts:
-
Rotor. This turns the shaft that delivers the mechanical power to the wheels.
-
Bearings. These support the rotor and allow it to rotate.
-
Stator. This is the stationary part of the electromagnetic current that surrounds the rotor.
-
Windings. These are coiled wires, wrapped around a magnetic core. They form magnetic poles when an electrical current passes through them.
-
Commutator. This is an electrical switch that supplies the current to the rotor.
Electric Car Battery Capacity Explained
Kilowatts (kW) is a unit of power, which is a measure of how much power something needs to run. A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of energy and shows how much energy has been used.
The battery capacity is measured in kWh. Lower powered EVs such as the Nissan Leaf stores 40kWh, whereas the Porsche Taycan Turbo S can store 93.4kWh.
The higher the kWh, the higher the range and the power.
How Does Braking Work in an Electric Car?
Electric cars use the same braking system as an ICE. This means they have brake pads and discs and need brake fluid to pressurise the system. The main difference between the systems is their efficiency. Thanks to ‘regenerative braking’, an electric car wastes less energy.
Braking in an ICE is inefficient. Not only do the brakes create friction, which produces heat as a waste product, but they also waste kinetic energy.
While an electric car still wastes heat through friction, it can recapture kinetic energy. It is stored in the batteries to be reused later. This improves the range and allows electric cars to travel further on a single charge.
Read More
How Much Does an Electric Car Cost?
If you’re starting to think about plugging into the electric revolution, you need to know what sort of budget you need before you can commit. Find out how much electric cars cost in this guide.
Why Would I Buy an Electric Car Over a Hybrid or Petrol/Diesel?
Electric power is clearly very different to standard fuel types. Is it worth taking the risk? Find out if an electric car is the best fuel source for you here.
How Far Can an Electric Car Go?
'Range Anxiety' has put many drivers off making the switch to an electric car. If you're worried that an EV won't go far enough on one charge, you're not alone. Read this guide to find out how far an electric car can go on one charge and why it's enough for the average daily commute.
Do Electric Cars Have Gears?
Electric cars and ICEs work in different ways. While you're used to dealing with a gearbox in your current car, you don't have to in an EV. Find out why they don't need gears and how they work instead in this guide.
Do Electric Cars Have an Exhaust?
As electric cars do not produce any emissions, there is no need for them to be fitted with exhausts. This article can tell you why the lack of an exhaust on an electric car is beneficial.
How to Drive an Electric Car
As electric cars work in a different way, you have to change your driving style to get the most out of them. Regenerative Braking is the biggest difference and it can significantly extend your EV's range if used correctly. Learn more about driving an electric car in this guide.
Is It Worth Making a Manual Electric Car?
Part of the appeal of an electric car is the absence of a manual transmission, as electric vehicles can maintain one speed without the need for changing gears. This article explores the concept of a manual electric car, and explains why this is unlikely to hit the market any time soon.