A catalytic converter is one of the most vital components in your car – yet you may know nothing about it.
All vehicles that are powered by an internal combustion engine (ICE) have catalytic converters which work to substantially reduce the levels of harmful pollutants produced by the exhaust.
Read on and find out what a catalytic converter is, what it does, and why catalytic converter theft is becoming a common occurrence these days.
Page Contents
- What Is a Catalytic Converter?
- What Does a Catalytic Converter Do?
- Does My Car Need a Catalytic Converter?
- What Does a Cat Converter Look Like?
- Where Would You Find a Catalytic Converter?
- Why Are Cat Converter Thefts So Common?
- What Are the Symptoms of a Bad Cat Converter?
- What Causes the Catalytic Converter to Wear Out?
- FAQs
What Is a Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is a part of the exhaust system.
It includes a core of ceramics with pores of less than 1mm.
These pores are coated with powdered catalysts containing metals like platinum, palladium and rhodium.
The pores heat up – as they are close to the engine – allowing the chemical structure of exhaust gases passing through to change.
Harmful gases are removed and converted into nitrogen and oxygen.
Carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons are converted into carbon dioxide and water.
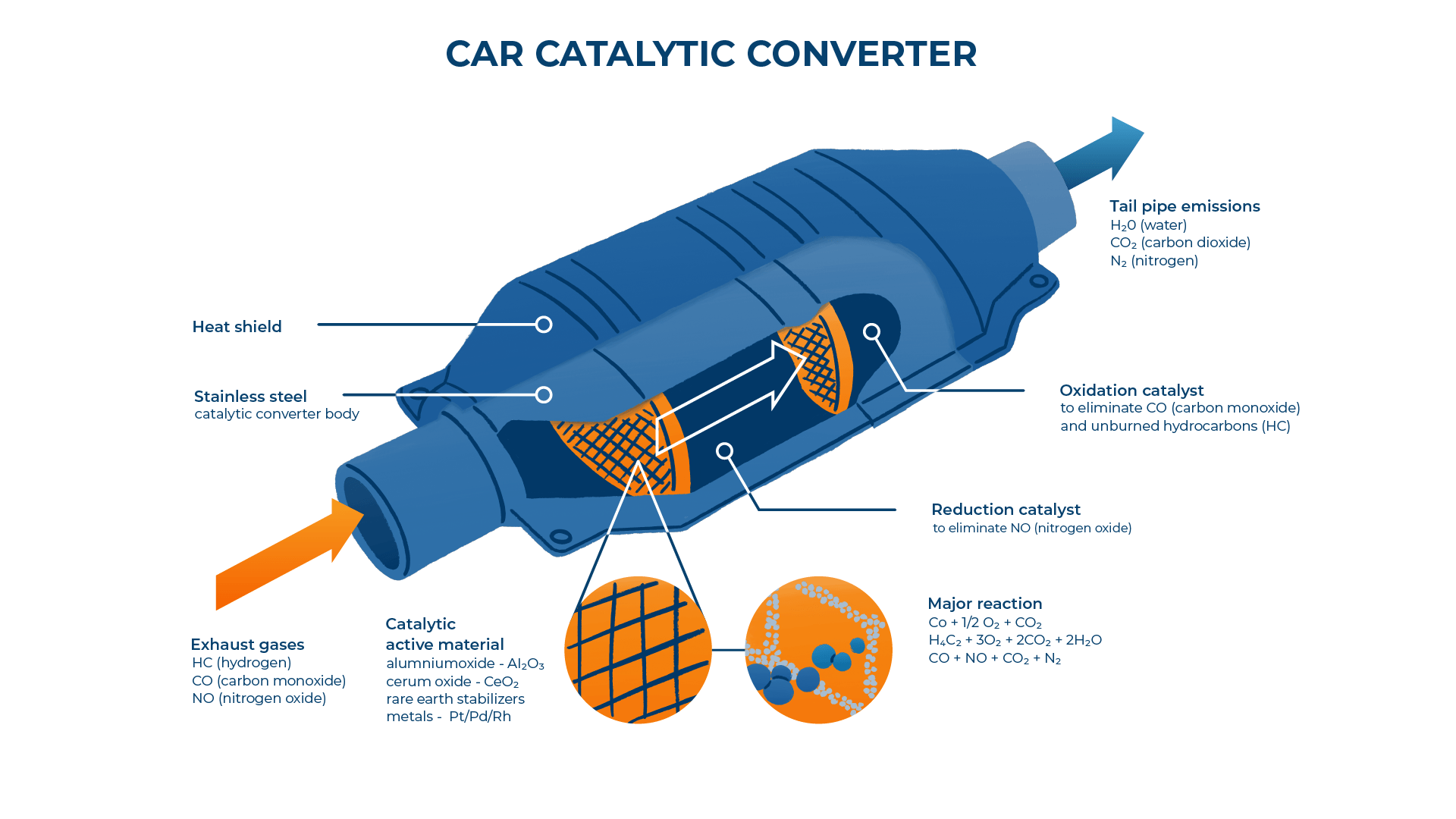
What Does a Catalytic Converter Do?
The catalytic converter speeds up the removal of harmful exhaust gases, by splitting their molecules up before they leave the exhaust.
It converts CO2 (carbon dioxide) and NOx (nitrogen oxides) into oxygen and water vapour.
These are much cleaner emissions, which are safer to release into the atmosphere.
Modern exhaust systems are designed to release the less harmful elements into the atmosphere separately.
Does My Car Need a Catalytic Converter?
Yes, your car needs a catalytic converter.
By law, every car registered in the UK must have one. This has been standard for petrol vehicles since 1992, and 2001 for diesel vehicles.
There are different types of catalytic converters for petrol and diesel engines, as they combust differently.
The three types of catalytic converters used in cars are:
- Oxidation catalyst (OC)
- Three-way Catalyst and Oxidation Catalyst (TWC-OC)
- Diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC)
Oxidation Catalyst (OC)
An OC uses oxygen as a catalyst, which reacts with carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons to form less harmful gases – like carbon dioxide and H2O.
Three-way Catalyst and Oxidation Catalyst (TWC-OC)
A three-way catalyst and oxidation catalyst combines the OC with a three-way catalyst.
The oxidation process converts hydrocarbons into H2O and other less harmful gases, and the three-way catalyst can convert the more potent gases.
Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC)
In diesel cars, a diesel oxidation catalyst is an aftertreatment component that converts carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water.
Diesel cars naturally produce more pollution than petrol cars.
To combat rising pollution levels, car companies have invented other exhaust treatments, including diesel particulate filters and AdBlue.
What Does a Cat Converter Look Like?
A catalytic converter looks like a large metal box with two pipes coming out of it.
Where Would You Find a Catalytic Converter?
It is bolted to the exhaust assembly underneath the back of your car.
If you can’t see it, you should have your car towed to a local garage right away as you may be the victim of catalytic converter theft which is becoming an increasing problem in the UK.
Why Are Cat Converter Thefts So Common?
Catalytic converter thefts are common in the UK because the catalyst materials have a very high value.
The part is also an easy target due to its location on the vehicle and how easy it is to access.
Thieves will cut the exhaust manifold away from the car and disassemble it later.
If you think you have been the victim of a catalytic converter theft, don’t drive the car.
Contact your recovery provider or get a local mechanic to tell you if your catalytic converter has been stolen.
You can report the crime to the police and will need to source a replacement catalytic converter.
If you can provide a valid crime number to your insurance company, then they should cover the cost of the replacement for you.
What Are the Symptoms of a Bad Cat Converter?
If you notice any of the following symptoms, then you may have a bad catalytic converter:
- An illuminated warning light
- Slower engine performance
- The engine cuts out
- Reduced acceleration range
- Increased fuel consumption
- Excessive white smoke
- Blue smoke
- A rattling noise from the exhaust
- Additional heat under your car
- Smell of rotten eggs from exhaust
- Dark smoke from exhaust
A damaged catalytic converter can cause the exhaust to become blocked and your engine to shut down entirely if you don’t book a replacement soon.
You may need to book a catalytic converter replacement - or your engine could shut down entirely.
What Causes the Catalytic Converter to Wear Out?
The following issues can cause your car’s catalytic converter to wear out sooner than necessary:
- Poor engine maintenance
- Using the wrong oil
- Coolant leaks
- Broken oxygen sensor
- Misfiring spark plugs
You may also wear the part out if you constantly use your vehicle for short trips.
The catalytic converter only works when it reaches a certain temperature. If it doesn't get hot enough, it will not burn the hydrocarbons completely.
It takes time for your car to reach this temperature – driving short distances will clog it.
Be sure to go for a longer drive regularly to burn off the deposits that build up in the converter.
By spotting an exhaust problem early, you can preserve your catalytic converter and increase your chances of passing the MOT emissions test.
If you have noticed any of these warning signs, then you should book a replacement soon to try and keep costs down.
Taking good care of your car and investing in regular maintenance is essential if you want to increase your vehicle's resale value.
FAQs








No comments yet
Leave a comment